
In this article, we examine several performance bonus examples that you can easily implement in your compensation plan today.
A payout in addition to their base salary can drive your team’s excellence and more importantly, retention. Unlock the secret to boosting employee performance with simple yet effective performance bonuses. From attendance to customer service, quality to safety, and team collaboration to individual contribution, these performance-based metrics can be used to reward certain aspects that lead to business success.
Related articles:
How to Achieve Effective Performance Management
5 Tips to Adjust Compensation and Performance
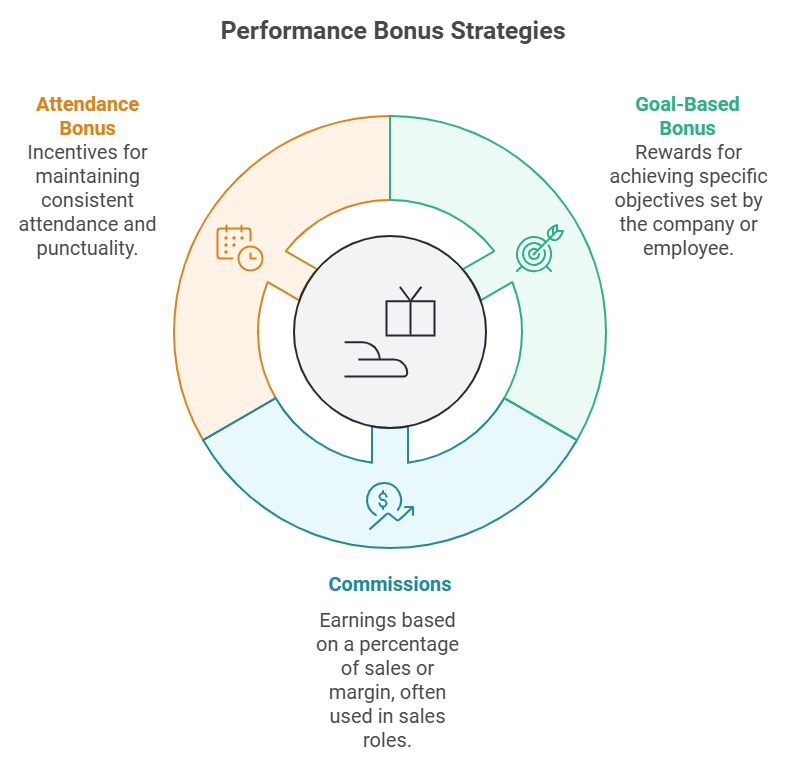
Individual Performance Bonus Examples
Goal-Based Bonus
This goal-based bonus system is based on the achievement of one or more objectives that were set for an individual employee or a team. These objectives are generally defined over a full year, but can also relate to a particular period. For example, you can set quarterly goals or semestrial goals.
A goal-based bonus is only relevant if the expected results are clearly defined, achievable and measurable. Sometimes the manager who defines it based on the overall business objectives, but often the employee also participates in setting their own objectives.
Goal-based performance can be tied to company goal. For example, many companies incentivize employees with a referral plan to hit their hiring goals. If an employee makes a referral for a successful hire, they receive a bonus amount paid to them.
Other than bonuses, consider providing personalized gifts to motivate and reward your employees, such as branded items like hoodies or phone cases. For those who love movies and music, you can consider gifting music & movies wall art canvas prints, which can add a personal touch to their workspace or home.
Commissions
This uncapped bonus, is generally linked to a defined percentage of sales or margin. The system is therefore quite simple to set up and explain to employees. This example of an individual performance bonus is often reserved for sales teams. It is very popular with salespeople because they are rewarded directly on their sales.
However, this type of bonus can discourage new employees who are not yet at the peak of their performance.
Attendance Bonus
An attendance bonus is a monetary incentive provided to employees based on their consistent attendance and punctuality. It is designed to motivate employees to maintain excellent attendance records by rewarding them for their reliability and dedication. The bonus can be awarded as a one-time payment or added to regular compensation, depending on the organization’s policies.
Implementing an attendance bonus would be best in organizations that highly value attendance and timeliness, especially in roles where absences can disrupt workflow, affect team dynamics, or hinder productivity. This is common in industries that operate on strict schedules for employees.
For example, in manufacturing, healthcare, customer service, and transportation, maintaining a full workforce is crucial for seamless operations and customer satisfaction. In such cases, managers may delegate the task of tracking attendance and administering bonuses to HR teams to ensure efficient execution of the process.
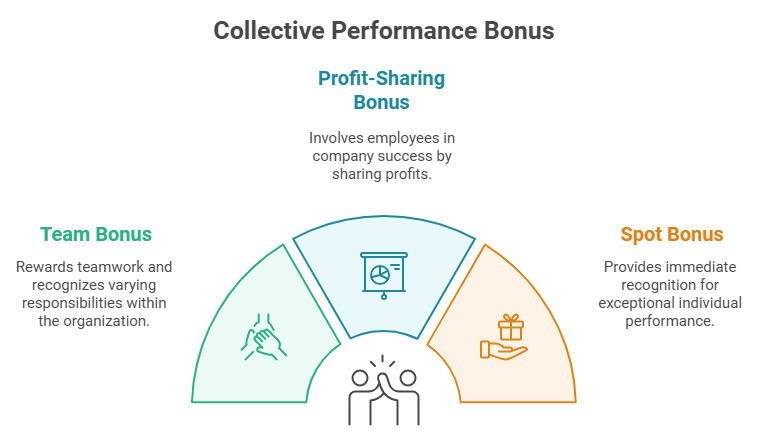
Collective Performance Bonus Examples
Team Bonus
When it comes to implementing team bonuses, HR professionals have the opportunity to customize them based on specific criteria. Here are two effective differentiating factors to consider:
Based on grade or role: Tailoring bonuses according to employee grade or role acknowledges the varying levels of responsibility within the organization. This approach ensures fairness and recognizes the impact different positions have on the company’s success. It motivates employees at all levels to contribute to team goals and projects.
Individual Contribution to the team: Many companies incorporate teamwork into their competency framework. They treat it as a fundamental skill that is recognized and rewarded through performance-based or contribution-based compensation.
Profit-Sharing Bonus
The idea behind profit-sharing bonuses is to reward and involve the employees in the company’s success. It’s like saying, “Hey, we did a great job together, and because of that, we all get rewarded!”
Implementing a profit-sharing bonus or stock options works best in companies where the employees’ efforts directly impact the company’s profitability. For example, if you work at a store and your hard work helps the store make more sales and earn more money, it would be fair to share some of that extra profit with you. A margin calculator can help determine the exact portion of profits available for sharing, ensuring that bonuses are distributed fairly and sustainably. This will help businesses strike a balance between rewarding employees and maintaining financial stability.
Profit-sharing bonuses can also encourage teamwork because everyone is working together to make the company successful. It’s like playing on a sports team and winning a game together. When the team wins, everyone feels happy and gets a reward for their contribution.
Spot Bonus
Spot bonuses are those that are given on a one-time basis and are normally discretionary. This would usually occur immediately after a notable achievement. Let’s say you work at a store, and one day you go above and beyond to help a customer who was having a difficult time. Your boss might notice your extra effort and decide to give you a spot bonus to show appreciation. Another example could be a bonus pay for volunteering to work overtime during a busy season.
You don’t know when you might receive a bonus, so it makes them even more exciting. They’re a way for employers or teachers to recognize and reward exceptional performance or behavior that goes beyond what is expected.
How to select a performance bonus to implement?
Individual performance bonuses are set up to reward employees individually. In addition to a fixed salary, this variable component of total compensation rewards the employee’s commitment or achieving their business objectives (e.g. their sales, new customer accounts). To choose which one will work best for your team, consider the different types and when they are most suitable.
Usually, organizations will implement a mix of different performance bonus types to align with their business goals, organizational structure and available resources.
How and when should bonuses be paid?
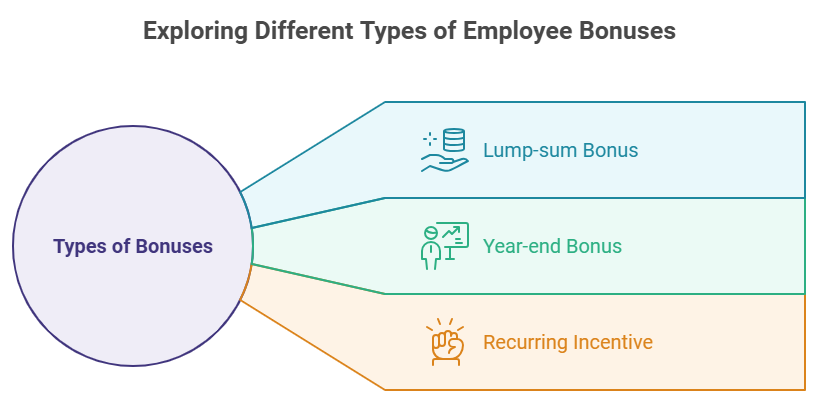
Lump-sum
A lump-sum bonus is a one-time payment given to an employee as a special reward or recognition for their performance, achievements, or contributions. It is usually a fixed amount of money that is given all at once. This type of bonus is not tied to a specific time period or ongoing performance. It’s like receiving a big gift or a cash prize for something exceptional you did.
Year-end
A year-end bonus, as the name suggests, is a bonus given to employees at the end of the year. It is often based on the company’s overall performance throughout the year or the individual’s performance during that time. The amount of the bonus can vary depending on factors such as company profits, individual goals, or performance evaluations. Year-end bonuses are a way for companies to show appreciation for the hard work and contributions of their employees over the course of a year.
Recurring Incentive
A recurring incentive is a type of bonus that is given on a regular basis, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. It is designed to motivate employees to consistently perform well or achieve certain targets over a specific period. Recurring incentives can be based on various performance metrics, such as sales targets, productivity, or meeting specific goals. Unlike lump-sum or year-end bonuses, recurring incentives provide ongoing motivation and rewards for sustained performance.
A Performance Software Adapted to your Needs
After examining these six performance bonus examples, you should now have a better idea of which ones will work best for your company. To implement a bonus structure into your incentive program, it is important to manage and automate them. This means being able to integrate it into your payroll and compensation tools.
Maybe you already have the tools you need. And maybe you will need a new tool to align with the new compensation plan you will implement. Either way, it is important to have a flexible HR ecosystem that allows you to adapt it to your needs.
PeopleSpheres is a flexible platform that allows you to unify all your most-trusted HR tools including your compensation and performance management software. With this platform, you have the freedom to switch out the tools as your business needs change.
As you consider reworking your compensation plan and bonus policy, remember that the policy is only as good as how you implement it.


-640x380.jpg)
